JS程序的入口,将当前APP对象注册到AppRegistry组件中,AppRegistry组件是js module
import { AppRegistry } from 'react-native'
...省略代码
AppRegistry.registerComponent('demo', () => Index)
# 启动流程
- 我们新建一个RN的项目,在原生代码中会生成
MainActivity和MainApplication两个Java类。顾名思义,MainAcitivity就是我们的Native的入口了, - 我们先来看下
MainApplication都做了哪些操作
public class MainApplication extends Application implements ReactApplication {
//ReactNativeHost:持有ReactInstanceManager实例,做一些初始化操作。
private final ReactNativeHost mReactNativeHost = new ReactNativeHost(this) {
@Override
public boolean getUseDeveloperSupport() {
return BuildConfig.DEBUG;
}
@Override
protected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {
return Arrays.<ReactPackage>asList(
new MainReactPackage()
);
}
};
@Override
public ReactNativeHost getReactNativeHost() {
return mReactNativeHost;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
//SoLoader:加载C++底层库,准备解析JS。
SoLoader.init(this, /* native exopackage */ false);
}
}
}
我们再来看下MainActivity的代码
public class MainActivity extends ReactActivity {
@Override
protected String getMainComponentName() {
return "demo";
}
}
可以看到其实是继承了
ReactActivity类,只是重写了getMainComponentName方法,有没有看出来,其方法的返回值和我们在JS端的值是一样的。如果不一致会怎么样,你可以自己试一下。
# ReactActivity
我们来看下
ReactActivity的方法的onCreate方法
public abstract class ReactActivity extends Activity
implements DefaultHardwareBackBtnHandler, PermissionAwareActivity {
private final ReactActivityDelegate mDelegate;
...省略代码
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
mDelegate.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
}
ReactActivity全权委托给ReactActivityDelegate来处理
ReactActivityDelegate
public class ReactActivityDelegate {
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 弹框权限判断
boolean needsOverlayPermission = false;
if (getReactNativeHost().getUseDeveloperSupport() && Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.M) {
// Get permission to show redbox in dev builds.
if (!Settings.canDrawOverlays(getContext())) {
needsOverlayPermission = true;
Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_MANAGE_OVERLAY_PERMISSION, Uri.parse("package:" + getContext().getPackageName()));
FLog.w(ReactConstants.TAG, REDBOX_PERMISSION_MESSAGE);
Toast.makeText(getContext(), REDBOX_PERMISSION_MESSAGE, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
((Activity) getContext()).startActivityForResult(serviceIntent, REQUEST_OVERLAY_PERMISSION_CODE);
}
}
// 加载组建逻辑 mMainComponentName为getMainComponentName返回的值
if (mMainComponentName != null && !needsOverlayPermission) {
loadApp(mMainComponentName);
}
// 双击判断工具类
mDoubleTapReloadRecognizer = new DoubleTapReloadRecognizer();
}
protected void loadApp(String appKey) {
//空判断
if (mReactRootView != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot loadApp while app is already running.");
}
// 创建 RN容器根视图
mReactRootView = createRootView();
mReactRootView.startReactApplication(
getReactNativeHost().getReactInstanceManager(),
appKey,
getLaunchOptions());
//将rootview添加入activity
getPlainActivity().setContentView(mReactRootView);
}
}
loadApp做了三件事:创建RootView、创建ReactApplication、创建ReactInstanceManager
# ReactRootView
ReactRootView是一个自定义的View,其父类是FrameLayout。因此,可以把RN看成是一个特殊的 “自定义View”。
我们来看下
startReactApplication方法
public void startReactApplication(
ReactInstanceManager reactInstanceManager,
String moduleName,
@Nullable Bundle initialProperties) {
...省略代码
try {
//在UI线程中进行
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
Assertions.assertCondition(
mReactInstanceManager == null,
"This root view has already been attached to a catalyst instance manager");
// 赋值
mReactInstanceManager = reactInstanceManager;
mJSModuleName = moduleName;
mAppProperties = initialProperties;
// 判断ReactContext是否初始化,没有就异步进行初始化
if (!mReactInstanceManager.hasStartedCreatingInitialContext()) {
mReactInstanceManager.createReactContextInBackground();
}
//宽高计算完成后添加布局监听
attachToReactInstanceManager();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
}
}
startReactApplication中的三个参数
| 形参 | 描述 |
|---|---|
reactInstanceManager | ReactInstanceManager类型,创建和管理CatalyInstance的实例 |
moduleName | 就是之前的组件名 |
initialProperties | 是Native向JS传递的数据,以后可能由POJO代替,默认是null,需要的话要重写createReactActivityDelegate ,并重写其中getLaunchOptions方法 |
startReactApplication中调用了ReactInstanceManager的createReactContextInBackground方法。
# ReactInstanceManager
public void createReactContextInBackground() {
//首次执行
mHasStartedCreatingInitialContext = true;
recreateReactContextInBackgroundInner();
}
该方法只会在
application中执行一次,JS重载时,会走recreateReactContextInBackground, 这两个方法最终都会调用recreateReactContextInBackgroundInner方法
@ThreadConfined(UI)
private void recreateReactContextInBackgroundInner() {
// 确保在UI线程中执行
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
if (mUseDeveloperSupport && mJSMainModuleName != null &&
!Systrace.isTracing(TRACE_TAG_REACT_APPS | TRACE_TAG_REACT_JSC_CALLS)) {
// 调试模式,加载服务器bundle
return;
}
// 加载本地bundle
recreateReactContextInBackgroundFromBundleLoader();
}
@ThreadConfined(UI)
private void recreateReactContextInBackgroundFromBundleLoader() {
recreateReactContextInBackground(
new JSCJavaScriptExecutor.Factory(mJSCConfig.getConfigMap()),
mBundleLoader);
}
| 形参 | 描述 |
|---|---|
jsExecutorFactory | C++和JS双向通信的中转站 |
jsBundleLoader | bundle加载器,根据ReactNativeHost中的配置决定从哪里加载bundle文件 |
private void recreateReactContextInBackground(
JavaScriptExecutor.Factory jsExecutorFactory,
JSBundleLoader jsBundleLoader) {
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
//创建ReactContextInitParams对象
final ReactContextInitParams initParams = new ReactContextInitParams(
jsExecutorFactory,
jsBundleLoader);
if (mCreateReactContextThread == null) {
// 新增线程初始化ReactContext
runCreateReactContextOnNewThread(initParams);
} else {
mPendingReactContextInitParams = initParams;
}
}
runCreateReactContextOnNewThread中有一个核心方法createReactContext来创建ReactContext
private ReactApplicationContext createReactContext(
JavaScriptExecutor jsExecutor,
JSBundleLoader jsBundleLoader) {
// 包装ApplicationContext
final ReactApplicationContext reactContext = new ReactApplicationContext(mApplicationContext);
//创建JavaModule注册表Builder,用来创建JavaModule注册表,JavaModule注册表将所有的JavaModule注册到CatalystInstance中。
NativeModuleRegistryBuilder nativeModuleRegistryBuilder = new NativeModuleRegistryBuilder(
reactContext,
this,
mLazyNativeModulesEnabled);
// 创建JavaScriptModule注册表Builder
JavaScriptModuleRegistry.Builder jsModulesBuilder = new JavaScriptModuleRegistry.Builder();
if (mUseDeveloperSupport) {
// 调试模式下,将错误交给DevSupportManager处理
reactContext.setNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler(mDevSupportManager);
}
...省略代码
try {
//创建CoreModulesPackage,其中封装了RN Framework核心功能,通信、调试等。
CoreModulesPackage coreModulesPackage =
new CoreModulesPackage(
this,
mBackBtnHandler,
mUIImplementationProvider,
mLazyViewManagersEnabled);
//把各自的Module添加到对应的注册表中
processPackage(coreModulesPackage, nativeModuleRegistryBuilder, jsModulesBuilder);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
}
// 将我们Application中的ReactPackage循环处理,加入对应的注册表中。
for (ReactPackage reactPackage : mPackages) {
...省略代码
try {
processPackage(reactPackage, nativeModuleRegistryBuilder, jsModulesBuilder);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
}
}
...省略代码
//生成Java注册表,将Java可调用的API暴露给JS
NativeModuleRegistry nativeModuleRegistry;
try {
nativeModuleRegistry = nativeModuleRegistryBuilder.build();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
ReactMarker.logMarker(BUILD_NATIVE_MODULE_REGISTRY_END);
}
NativeModuleCallExceptionHandler exceptionHandler = mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler != null
? mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler
: mDevSupportManager;
//构建CatalystInstanceImpl实例
CatalystInstanceImpl.Builder catalystInstanceBuilder = new CatalystInstanceImpl.Builder()
.setReactQueueConfigurationSpec(mUseSeparateUIBackgroundThread ?
ReactQueueConfigurationSpec.createWithSeparateUIBackgroundThread() :
ReactQueueConfigurationSpec.createDefault())
//JS执行通信类
.setJSExecutor(jsExecutor)
//Java模块注册表
.setRegistry(nativeModuleRegistry)
// JS注册表
.setJSModuleRegistry(jsModulesBuilder.build())
// Bundle加载工具类
.setJSBundleLoader(jsBundleLoader)
// 异常处理器
.setNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler(exceptionHandler);
// 省略代码
final CatalystInstance catalystInstance;
try {
catalystInstance = catalystInstanceBuilder.build();
} finally {
//省略代码
}
if (mBridgeIdleDebugListener != null) {
catalystInstance.addBridgeIdleDebugListener(mBridgeIdleDebugListener);
}
if (Systrace.isTracing(TRACE_TAG_REACT_APPS | TRACE_TAG_REACT_JSC_CALLS)) {
//调用CatalystInstanceImpl的Native方法把Java Registry转换为Json,再由C++层传送到JS层。 catalystInstance.setGlobalVariable("__RCTProfileIsProfiling", "true");
}
//关联ReacContext与CatalystInstance
reactContext.initializeWithInstance(catalystInstance);
//通过CatalystInstance开始加载JS Bundle
catalystInstance.runJSBundle();
return reactContext;
}
这段代码比较长,它主要做了这几件事:
- 创建
JavaModule注册表和JavaScriptModule注册表,交给CatalystInstance管理。 - 处理
ReactPackage,将各自的Module放入对应的注册表中。 - 通过上面的各个参数创建
CatalystInstance实例。CatalystInstance关联ReactContext,开始加载JS Bundle
# CatalystInstance
我们来看下
CatalystInstance的实现类CatalystInstanceImpl的构造方法
private CatalystInstanceImpl(
final ReactQueueConfigurationSpec reactQueueConfigurationSpec,
final JavaScriptExecutor jsExecutor,
final NativeModuleRegistry registry,
final JavaScriptModuleRegistry jsModuleRegistry,
final JSBundleLoader jsBundleLoader,
NativeModuleCallExceptionHandler nativeModuleCallExceptionHandler) {
//用来创建JNI相关方法,并返回mHybridData
mHybridData = initHybrid();
// Android UI线程、JS线程、NativeMOdulesQueue线程
mReactQueueConfiguration = ReactQueueConfigurationImpl.create(
reactQueueConfigurationSpec,
new NativeExceptionHandler());
// 省略代码
//调用 C++ 层代码进行初始化Bridge
initializeBridge(
new BridgeCallback(this),
jsExecutor,
mReactQueueConfiguration.getJSQueueThread(),
mNativeModulesQueueThread,
mUIBackgroundQueueThread,
mJavaRegistry.getJavaModules(this),
mJavaRegistry.getCxxModules());
}
private native void initializeBridge(
ReactCallback callback,
JavaScriptExecutor jsExecutor,
MessageQueueThread jsQueue,
MessageQueueThread moduleQueue,
MessageQueueThread uiBackgroundQueue,
Collection<JavaModuleWrapper> javaModules,
Collection<ModuleHolder> cxxModules);
| 形参 | 描述 |
|---|---|
ReactCallback | CatalystInstanceImpl的静态内部类ReactCallback,负责接口回调 |
JavaScriptExecutor | JS执行器,将JS的调用传给C++层 |
MessageQueueThread | JS线程 |
MessageQueueThread moduleQueue | Java线程 |
MessageQueueThread uiBackgroundQueue | UI背景线程 |
javaModules | java module |
cxxModules | c++ module |
createReactContext方法中用catalystInstance.runJSBundle()来加载JS bundle
@Override
public void runJSBundle() {
...
mJSBundleLoader.loadScript(CatalystInstanceImpl.this);
...
}
# JSBundleLoader
CatalystInstanceImpl.runJSBundle()会调用JSBundleLoader去加载JS Bundle,由于不同的情况可能会有不同的JSBundleLoader,我们假设其中一种
public abstract class JSBundleLoader {
/**
* This loader is recommended one for release version of your app. In that case local JS executor
* should be used. JS bundle will be read from assets in native code to save on passing large
* strings from java to native memory.
*/
public static JSBundleLoader createAssetLoader(
final Context context,
final String assetUrl,
final boolean loadSynchronously) {
return new JSBundleLoader() {
@Override
public String loadScript(CatalystInstanceImpl instance) {
instance.loadScriptFromAssets(context.getAssets(), assetUrl, loadSynchronously);
return assetUrl;
}
};
}
可以看到它会继续调用
CatalystInstance中的loadScriptFromAssets方法
public class CatalystInstanceImpl {
/* package */ void loadScriptFromAssets(AssetManager assetManager, String assetURL) {
mSourceURL = assetURL;
jniLoadScriptFromAssets(assetManager, assetURL);
}
private native void jniLoadScriptFromAssets(AssetManager assetManager, String assetURL);
}
最终呢,还是会调用
CatalystInstanceImpl.cpp去加载JS Bundle,我们去C++层看一下实现
我们先看下源码的结构图
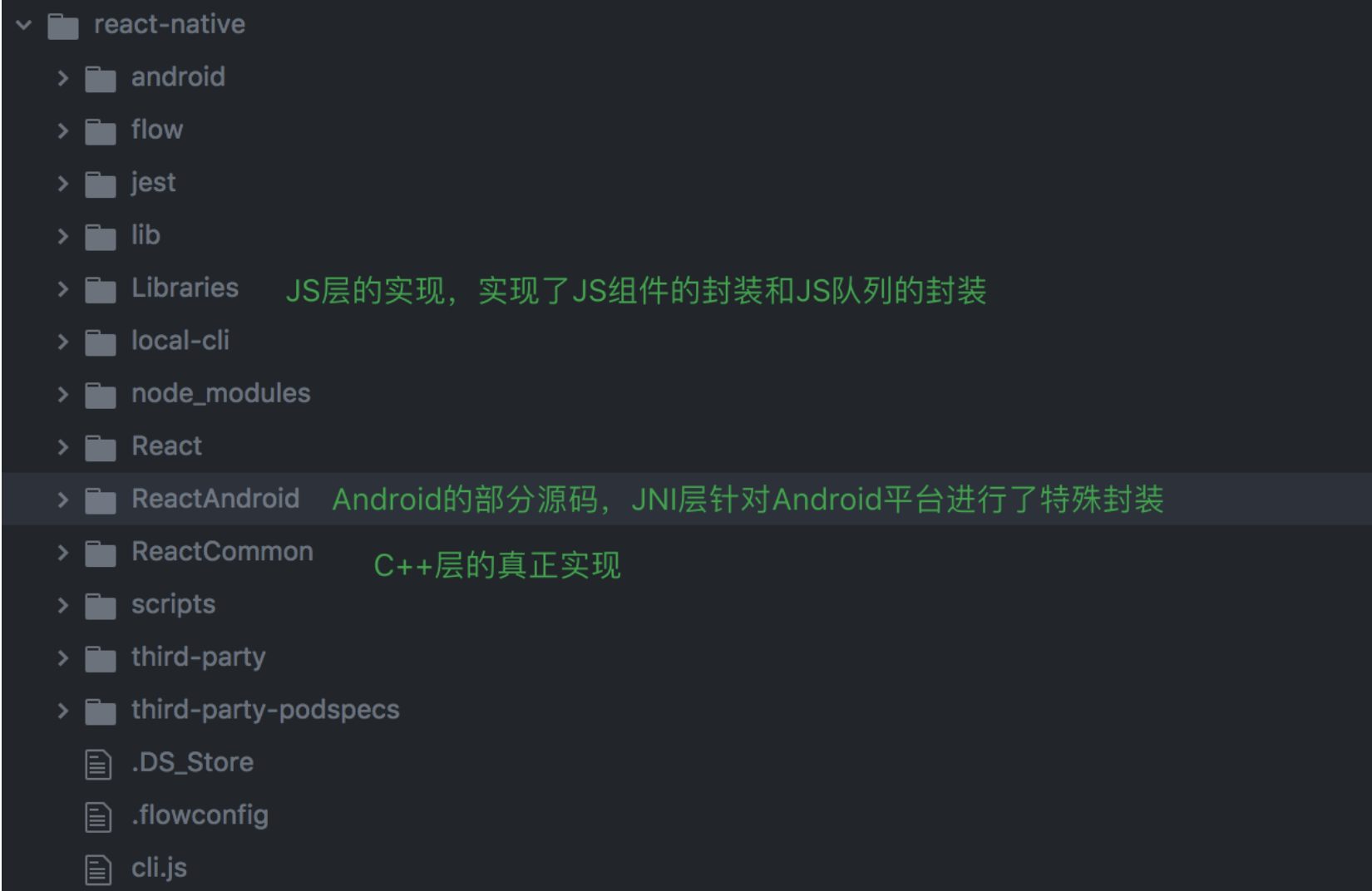
# CatalystInstanceImpl.cpp
在ReactAndroid的Jni中,我们看下相关代码:
void CatalystInstanceImpl::jniLoadScriptFromAssets(
jni::alias_ref<JAssetManager::javaobject> assetManager,
const std::string& assetURL,
bool loadSynchronously) {
const int kAssetsLength = 9; // strlen("assets://");
// 获取soure js Bundle的路径名
auto sourceURL = assetURL.substr(kAssetsLength);
// 获取AssetManager
auto manager = extractAssetManager(assetManager);
// 读取JS Bundle里的内容
auto script = loadScriptFromAssets(manager, sourceURL);
// unbundle命令打包判断
if (JniJSModulesUnbundle::isUnbundle(manager, sourceURL)) {
instance_->loadUnbundle(
folly::make_unique<JniJSModulesUnbundle>(manager, sourceURL),
std::move(script),
sourceURL,
loadSynchronously);
return;
} else {
//bundle命令打包走次流程,instance_是Instan.h中类的实例
instance_->loadScriptFromString(std::move(script), sourceURL, loadSynchronously);
}
}
# Instance.cpp
void Instance::loadScriptFromString(std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> string,
std::string sourceURL,
bool loadSynchronously) {
SystraceSection s("reactbridge_xplat_loadScriptFromString", "sourceURL", sourceURL);
if (loadSynchronously) {
loadApplicationSync(nullptr, std::move(string), std::move(sourceURL));
} else {
loadApplication(nullptr, std::move(string), std::move(sourceURL));
}
}
void Instance::loadApplicationSync(
std::unique_ptr<JSModulesUnbundle> unbundle,
std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> string,
std::string sourceURL) {
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(m_syncMutex);
m_syncCV.wait(lock, [this] { return m_syncReady; });
SystraceSection s("reactbridge_xplat_loadApplicationSync", "sourceURL", sourceURL);
//nativeToJsBridge_也是在Instance::initializeBridget()方法里初始化的,具体实现在NativeToJsBridge.cpp里。
nativeToJsBridge_->loadApplicationSync(std::move(unbundle), std::move(string), std::move(sourceURL));
}
NativeToJsBridge.cpp
void NativeToJsBridge::loadApplication(
std::unique_ptr<JSModulesUnbundle> unbundle,
std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> startupScript,
std::string startupScriptSourceURL) {
//获取一个MessageQueueThread,探后在线程中执行一个Task。
runOnExecutorQueue(
m_mainExecutorToken,
[unbundleWrap=folly::makeMoveWrapper(std::move(unbundle)),
startupScript=folly::makeMoveWrapper(std::move(startupScript)),
startupScriptSourceURL=std::move(startupScriptSourceURL)]
(JSExecutor* executor) mutable {
auto unbundle = unbundleWrap.move();
if (unbundle) {
executor->setJSModulesUnbundle(std::move(unbundle));
}
//executor从runOnExecutorQueue()返回的map中取得,与OnLoad中的JSCJavaScriptExecutorHolder对应,也与
//Java中的JSCJavaScriptExecutor对应。它的实例在JSExecutor.cpp中实现。
executor->loadApplicationScript(std::move(*startupScript),
std::move(startupScriptSourceURL));
});
}
unbundle命令,使用方式和bundle命令完全相同。unbundle命令是在bundle命令的基础上增加了一项功能,除了生成整合JS文件index.android.bundle外,还会 生成各个单独的未整合JS文件(但会被优化),全部放在js-modules目录下,同时会生成一个名为UNBUNDLE的标识文件,一并放在其中。UNBUNDLE标识文件的前4个字节 固定为0xFB0BD1E5,用于加载前的校验。
- 该函数进一步调用
JSExecutor.cpp的loadApplicationScript()方法。 - 到了这个方法,就是去真正加载JS文件了。
JSCExecutor.cpp
void JSCExecutor::loadApplicationScript(std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> script, std::string sourceURL) {
...
//使用Webkit JSC去解释执行JS
evaluateSourceCode(m_context, bcSourceCode, jsSourceURL);
flush();
}
void JSCExecutor::flush() {
...
//绑定bridge,核心就是通过getGlobalObject()将JS与C++通过Webkit jSC实现绑定
bindBridge();
//返回给callNativeModules
callNativeModules(m_flushedQueueJS->callAsFunction({}));
...
}
void JSCExecutor::callNativeModules(Value&& value) {
...
//把JS层相关通信数据转换为JSON格式
auto calls = value.toJSONString();
//m_delegate为JsToNativeBridge对象。
m_delegate->callNativeModules(*this, folly::parseJson(calls), true);
...
}
m_flushedQueueJS支线的是MessageQueue.js的flushedQueue()方法,此时JS已经被加载到队列中,等待Java层来驱动它。JS Bundle加载并解析完成后,我们回到Java代码中看看后续的流程- 我们在之前的
runCreateReactContextOnNewThread方法中,在creatReactContext之后还有一句核心的代码
setupReactContext(reactApplicationContext);
这就是加载
JS Bundle之后执行的代码
public class ReactInstanceManager {
private void setupReactContext(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
...
// Native Java module初始化
catalystInstance.initialize();
//重置ReactContext
mDevSupportManager.onNewReactContextCreated(reactContext);
//内存状态回调设置 mMemoryPressureRouter.addMemoryPressureListener(catalystInstance);
// 复位生命周期
moveReactContextToCurrentLifecycleState();
ReactMarker.logMarker(ATTACH_MEASURED_ROOT_VIEWS_START);
synchronized (mAttachedRootViews) {
//mAttachedRootViews保存的是ReactRootView
for (ReactRootView rootView : mAttachedRootViews) {
attachRootViewToInstance(rootView, catalystInstance);
}
}
...
}
}
private void attachMeasuredRootViewToInstance ( final ReactRootView rootView,
CatalystInstance catalystInstance) {
...
//将ReactRootView作为根布局
UIManagerModule uiManagerModule = catalystInstance.getNativeModule(UIManagerModule.class);
int rootTag = uiManagerModule.addMeasuredRootView(rootView);
//设置相关
rootView.setRootViewTag(rootTag);
rootView.runApplication();
...
}
/* package */ void runApplication() {
...
CatalystInstance catalystInstance = reactContext.getCatalystInstance();
WritableNativeMap appParams = new WritableNativeMap();
appParams.putDouble("rootTag", getRootViewTag());
@Nullable Bundle appProperties = getAppProperties();
if (appProperties != null) {
appParams.putMap("initialProps", Arguments.fromBundle(appProperties));
}
String jsAppModuleName = getJSModuleName();
//启动流程入口:由Java层调用启动
catalystInstance.getJSModule(AppRegistry.class).runApplication(jsAppModuleName, appParams);
...
}
可以看到,最终调用的是
catalystInstance.getJSModule(AppRegistry.class).runApplication(jsAppModuleName, appParams),AppRegistry.class是JS层暴露给Java层的接口方法。它的真正实现在AppRegistry.js里,AppRegistry.js是运行所有RN应用的JS层入口,我们来看看它的实现:
- 在
Libraries/ReactNative中的AppRegistry.js
# AppRegistry.js
runApplication(appKey: string, appParameters: any): void {
const msg =
'Running application "' + appKey + '" with appParams: ' +
JSON.stringify(appParameters) + '. ' +
'__DEV__ === ' + String(__DEV__) +
', development-level warning are ' + (__DEV__ ? 'ON' : 'OFF') +
', performance optimizations are ' + (__DEV__ ? 'OFF' : 'ON');
infoLog(msg);
BugReporting.addSource('AppRegistry.runApplication' + runCount++, () => msg);
invariant(
runnables[appKey] && runnables[appKey].run,
'Application ' + appKey + ' has not been registered.\n\n' +
'Hint: This error often happens when you\'re running the packager ' +
'(local dev server) from a wrong folder. For example you have ' +
'multiple apps and the packager is still running for the app you ' +
'were working on before.\nIf this is the case, simply kill the old ' +
'packager instance (e.g. close the packager terminal window) ' +
'and start the packager in the correct app folder (e.g. cd into app ' +
'folder and run \'npm start\').\n\n' +
'This error can also happen due to a require() error during ' +
'initialization or failure to call AppRegistry.registerComponent.\n\n'
);
SceneTracker.setActiveScene({name: appKey});
runnables[appKey].run(appParameters);
}
- 到这里就会去调用JS进行渲染,在通过
UIManagerModule将JS组件转换成Android组件,最终显示在ReactRootView上。 - 最后总结一下,就是先在应用终端启动并创建上下文对象,启动
JS Runtime,进行布局,将JS端的代码通过C++层,UIManagerMoodule转化成Android组件,再进行渲染,最后将渲染的View添加到ReactRootView上,最终呈现在用户面前。
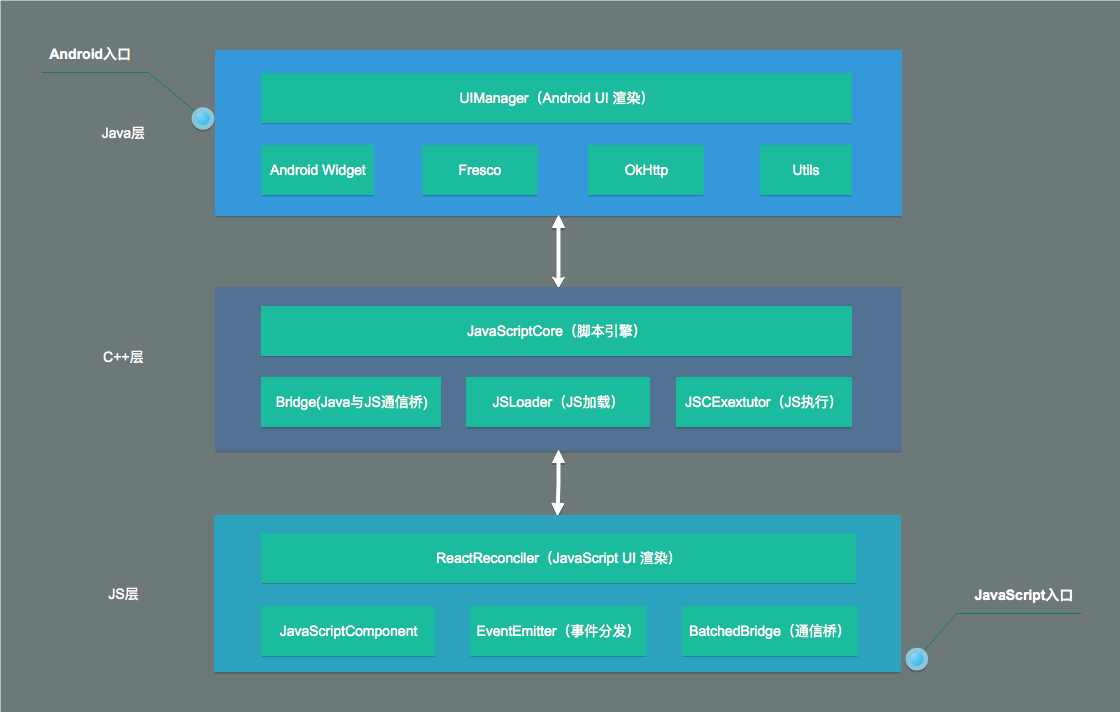
# 系统框架图
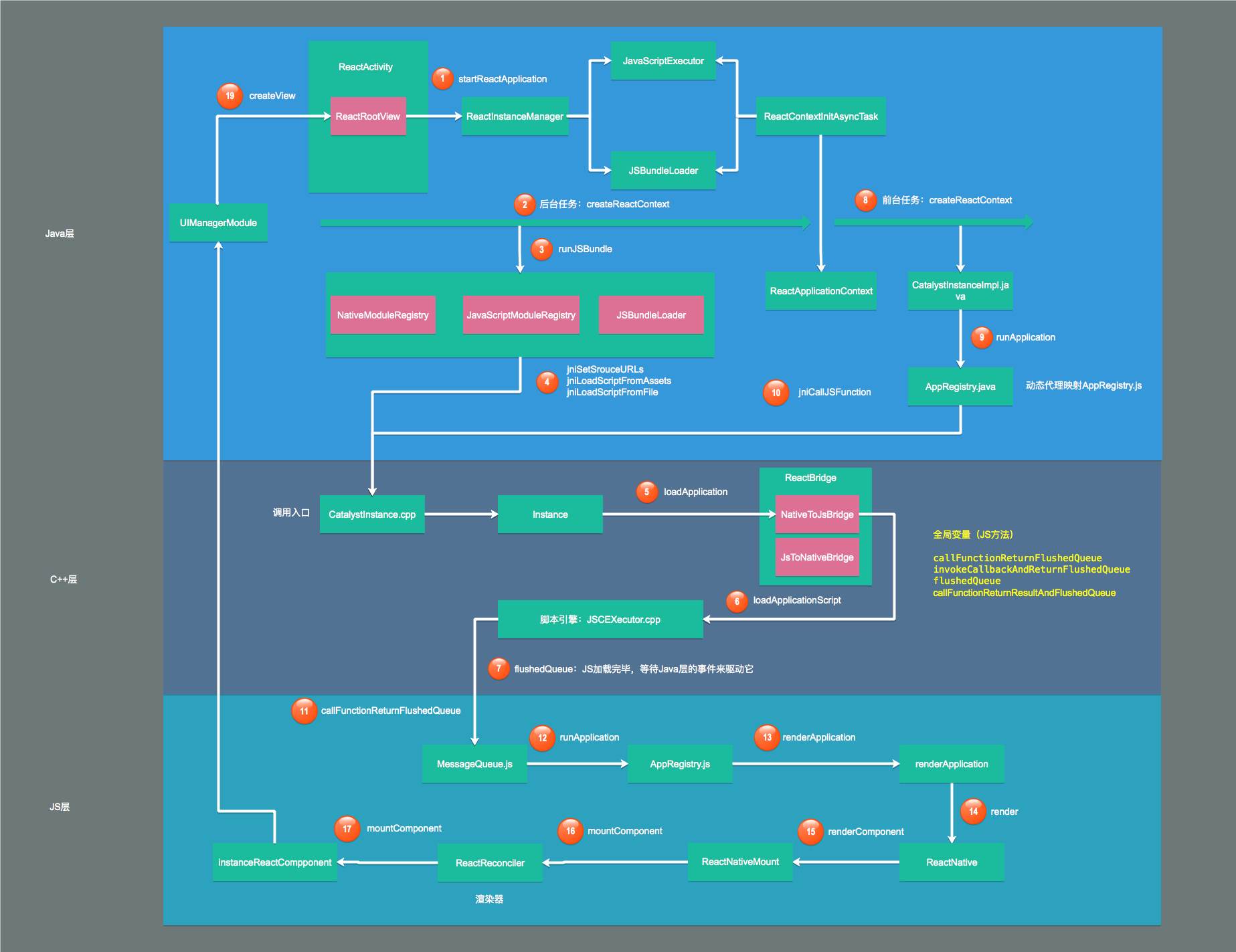
# 启动流程图