了解vuex核心概念请移步 https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/
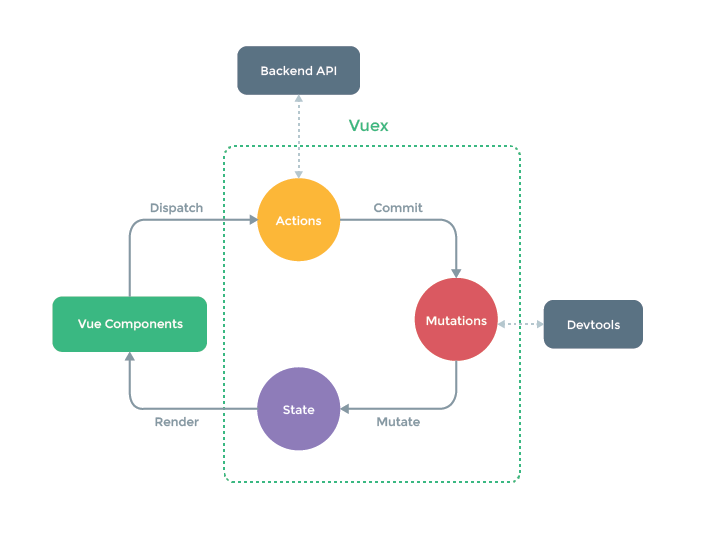
# 一、初始vuex
# 1.1 vuex是什么
vuex就是把需要共享的变量全部存储在一个对象里面,然后将这个对象放在顶层组件中供其他组件使用- 父子组件通信时,我们通常会采用
props + emit这种方式。但当通信双方不是父子组件甚至压根不存在相关联系,或者一个状态需要共享给多个组件时,就会非常麻烦,数据也会相当难维护
# 1.2 vuex中有什么
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
name: 'weish',
age: 22
},
getters: {
personInfo(state) {
return `My name is ${state.name}, I am ${state.age}`;
}
}
mutations: {
SET_AGE(state, age) {
commit(age, age);
}
},
actions: {
nameAsyn({commit}) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('SET_AGE', 18);
}, 1000);
}
},
modules: {
a: modulesA
}
}
个就是最基本也是完整的
vuex代码;vuex包含有五个基本的对象
state:存储状态。也就是变量;getters:派生状态。也就是set、get中的get,有两个可选参数:state、getters分别可以获取state中的变量和其他的getters。外部调用方式:store.getters.personInfo()。就和vue的computed差不多;mutations:提交状态修改。也就是set、get中的set,这是vuex中唯一修改state的方式,但不支持异步操作。第一个参数默认是state。外部调用方式:store.commit('SET_AGE', 18)。和vue中的methods类似。actions:和mutations类似。不过actions支持异步操作。第一个参数默认是和store具有相同参数属性的对象。外部调用方式:store.dispatch('nameAsyn')。modules:store的子模块,内容就相当于是store的一个实例。调用方式和前面介绍的相似,只是要加上当前子模块名,如:store.a.getters.xxx()
# 1.3 vue-cli中使用vuex的方式
目录结构
├── index.html
├── main.js
├── components
└── store
├── index.js # 我们组装模块并导出 store 的地方
├── state.js # 跟级别的 state
├── getters.js # 跟级别的 getter
├── mutation-types.js # 根级别的mutations名称(官方推荐mutions方法名使用大写)
├── mutations.js # 根级别的 mutation
├── actions.js # 根级别的 action
└── modules
├── m1.js # 模块1
└── m2.js # 模块2
state示例
const state = {
name: 'weish',
age: 22
};
export default state;
getter示例
getters.js示例(我们一般使用getters来获取state的状态,而不是直接使用state)
export const name = (state) => {
return state.name;
}
export const age = (state) => {
return state.age
}
export const other = (state) => {
return `My name is ${state.name}, I am ${state.age}.`;
}
mutation-type示例
将所有
mutations的函数名放在这个文件里
export const SET_NAME = 'SET_NAME';
export const SET_AGE = 'SET_AGE';
mutations示例
import * as types from './mutation-type.js';
export default {
[types.SET_NAME](state, name) {
state.name = name;
},
[types.SET_AGE](state, age) {
state.age = age;
}
};
actions示例
异步操作、多个
commit时
import * as types from './mutation-type.js';
export default {
nameAsyn({commit}, {age, name}) {
commit(types.SET_NAME, name);
commit(types.SET_AGE, age);
}
}
modules--m1.js示例
如果不是很复杂的应用,一般来讲是不会分模块的
export default {
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {}
}
index.js示例(组装vuex)
import vue from 'vue';
import vuex from 'vuex';
import state from './state.js';
import * as getters from './getters.js';
import mutations from './mutations.js';
import actions from './actions.js';
import m1 from './modules/m1.js';
import m2 from './modules/m2.js';
import createLogger from 'vuex/dist/logger'; // 修改日志
vue.use(vuex);
const debug = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'; // 开发环境中为true,否则为false
export default new vuex.Store({
state,
getters,
mutations,
actions,
modules: {
m1,
m2
},
plugins: debug ? [createLogger()] : [] // 开发环境下显示vuex的状态修改
});
最后将
store实例挂载到main.js里面的vue上去就行了
import store from './store/index.js';
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
render: h => h(App)
});
在
vue组件中使用时,我们通常会使用mapGetters、mapActions、mapMutations,然后就可以按照vue调用methods和computed的方式去调用这些变量或函数,示例如
import {mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions} from 'vuex';
/* 只写组件中的script部分 */
export default {
computed: {
...mapGetters([
name,
age
])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations({
setName: 'SET_NAME',
setAge: 'SET_AGE'
}),
...mapActions([
nameAsyn
])
}
};
# 二、modules
在 src 目录下 , 新建一个 store 文件夹 , 然后在里面新建一个 index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(vuex);
export default new vuex.Store({
state:{
show:false
}
})
在
main.js里的代码应该改成,在实例化Vue对象时加入store对象
//vuex
import store from './store'
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,//使用store
template: '<App/>',
components: { App }
})
这样就把
store分离出去了 , 那么还有一个问题是 : 这里$store.state.show无论哪个组件都可以使用 , 那组件多了之后 , 状态也多了 , 这么多状态都堆在 store 文件夹下的index.js不好维护怎么办 ?
- 我们可以使用
vuex的modules, 把store文件夹下的index.js改成
import Vue from 'vue'
import vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(vuex);
import dialog_store from '../components/dialog_store.js';//引入某个store对象
export default new vuex.Store({
modules: {
dialog: dialog_store
}
})
这里我们引用了一个
dialog_store.js, 在这个js文件里我们就可以单独写dialog组件的状态了
export default {
state:{
show:false
}
}
做出这样的修改之后 , 我们将之前我们使用的
$store.state.show统统改为$store.state.dialog.show即可
- 如果还有其他的组件需要使用
vuex, 就新建一个对应的状态文件 , 然后将他们加入store文件夹下的index.js文件中的modules中
modules: {
dialog: dialog_store,
other: other,//其他组件
}
# 三、mutations
对
vuex的依赖仅仅只有一个$store.state.dialog.show一个状态 , 但是如果我们要进行一个操作 , 需要依赖很多很多个状态 , 那管理起来又麻烦了
mutations里的操作必须是同步的
export default {
state:{//state
show:false
},
mutations:{
switch_dialog(state){//这里的state对应着上面这个state
state.show = state.show?false:true;
//你还可以在这里执行其他的操作改变state
}
}
}
使用
mutations后 , 原先我们的父组件可以改为
<template>
<div id="app">
<a href="javascript:;" @click="$store.commit('switch_dialog')">点击</a>
<t-dialog></t-dialog>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import dialog from './components/dialog.vue'
export default {
components:{
"t-dialog":dialog
}
}
</script>
使用
$store.commit('switch_dialog')来触发mutations中的switch_dialog方法
# 四、actions
多个
state的操作 , 使用mutations会来触发会比较好维护 , 那么需要执行多个mutations就需要用action了
export default {
state:{//state
show:false
},
mutations:{
switch_dialog(state){//这里的state对应着上面这个state
state.show = state.show?false:true;
//你还可以在这里执行其他的操作改变state
}
},
actions:{
switch_dialog(context){//这里的context和我们使用的$store拥有相同的对象和方法
context.commit('switch_dialog');
//你还可以在这里触发其他的mutations方法
},
}
}
那么 , 在之前的父组件中 , 我们需要做修改 , 来触发
action里的switch_dialog方法
<template>
<div id="app">
<a href="javascript:;" @click="$store.dispatch('switch_dialog')">点击</a>
<t-dialog></t-dialog>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import dialog from './components/dialog.vue'
export default {
components:{
"t-dialog":dialog
}
}
</script>
- 使用
$store.dispatch('switch_dialog')来触发action中的switch_dialog方法。 - 官方推荐 , 将异步操作放在
action中
# 五、getters
getters和vue中的computed类似 , 都是用来计算state然后生成新的数据 ( 状态 ) 的
- 假如我们需要一个与状态
show刚好相反的状态 , 使用vue中的computed可以这样算出来
computed(){
not_show(){
return !this.$store.state.dialog.show;
}
}
那么 , 如果很多很多个组件中都需要用到这个与
show刚好相反的状态 , 那么我们需要写很多很多个not_show, 使用getters就可以解决这种问题
export default {
state:{//state
show:false
},
getters:{
not_show(state){//这里的state对应着上面这个state
return !state.show;
}
},
mutations:{
switch_dialog(state){//这里的state对应着上面这个state
state.show = state.show?false:true;
//你还可以在这里执行其他的操作改变state
}
},
actions:{
switch_dialog(context){//这里的context和我们使用的$store拥有相同的对象和方法
context.commit('switch_dialog');
//你还可以在这里触发其他的mutations方法
},
}
}
我们在组件中使用
$store.state.dialog.show来获得状态show, 类似的 , 我们可以使用$store.getters.not_show来获得状态not_show
- 注意 :
$store.getters.not_show的值是不能直接修改的 , 需要对应的state发生变化才能修改
# 六、mapState、mapGetters、mapActions
很多时候 ,
$store.state.dialog.show、$store.dispatch('switch_dialog')这种写法很不方便
- 使用
mapState、mapGetters、mapActions就不会这么复杂了
<template>
<el-dialog :visible.sync="show"></el-dialog>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex';
export default {
computed:{
//这里的三点叫做 : 扩展运算符
...mapState({
show:state=>state.dialog.show
}),
}
}
</script>
相当于
<template>
<el-dialog :visible.sync="show"></el-dialog>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex';
export default {
computed:{
show(){
return this.$store.state.dialog.show;
}
}
}
</script>
mapGetters、mapActions和mapState类似 ,mapGetters一般也写在computed中 ,mapActions一般写在methods中